The Difference Between Rapid Antigen Test And PCR

Many people across the nation now routinely undergo COVID-19 testing. Both those who have received the vaccine and those who have not are increasingly depending on weekly (often daily) test to go to work, travel, or interact with the community as the Omicron variety of the SARS-CoV-2 virus emerges as the predominant strain.
The abrupt COVID-19 viral epidemic throws the world into disarray. It severely threatens human health because it is a highly contagious respiratory disease. Early buy rapid antigen test and diagnosis of the virulent should be the first course of action when a highly infectious disease outbreak begins.
Early testing enables swift identification of sick individuals, prompt treatment, and implementation of all essential control measures to stop the spread of the diseases. Click here to know the different types of COVID rapid antigen tests.
The COVID-19 test can identify the SARS-CoV-2 virus and the human systems’ antibodies in response to infections or vaccinations. The following are the primary molecular assays used to detect COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) infection:
- Molecular tests include RT-PCR and NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test)
- Immunogen test
- Testing antibodies
Each test picks up a different aspect of the infection, making them all unique. In these tests, test speed and accuracy are also different.
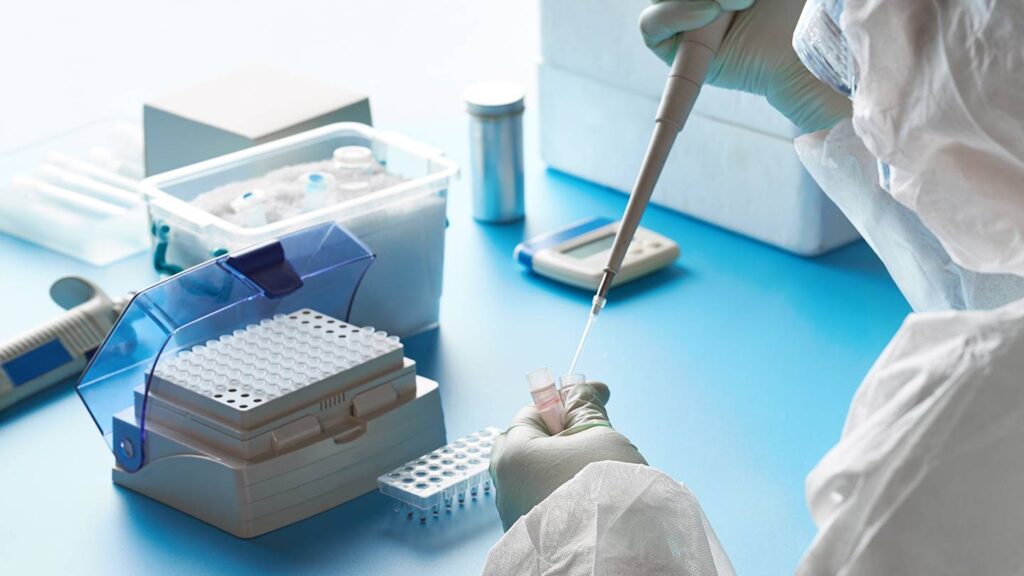
Currently, two broad testing categories are available to the public: PCR and antigen tests. They are both considered ‘diagnostic tests,’ which means either will be able to tell you if you are currently infected with the coronavirus at the time of testing. Early detection of illnesses, rapid treatment, and execution of all necessary control measures to halt the spread of the diseases are all made possible by early testing.
The COVID-19 test can detect antibodies produced by human systems in response to illnesses or vaccines and the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The main molecular tests for identifying COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) infection are as follows:
- RT-PCR and NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test) are two examples of molecular tests. Immunogen tests check for antibodies.
- Every test is distinct because it detects a different element of the virus. These tests also differ in terms of test speed and accuracy.
What Is A PCR Test?
It’s a test to identify genetic material from a particular organism, such as a virus; a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test is conducted. If you are already infected with a virus at the time of the test, the test will reveal its presence. Even when you are no longer sick, the test may still be able to find viral pieces.
PCRs can determine whether a virus is present by looking for the virus’s genetic material. The time between testing and receiving a convincing result is the only disadvantage of PCR tests. In general, PCR testing is exact.
A sample is taken and then sent to a lab for analysis (often using the deep nasal swab technique, although samples from the throat or saliva may also be analyzed). That procedure typically takes one to three days.
Disadvantages of PCR
While a PCR test is ideal for identifying COVID-19, getting one is not always straightforward. Perhaps you will have to wait a few days to learn if you are positive or negative after a PCR test because it needs to be performed by a medical professional and doesn’t produce findings immediately.
What Is An Antigen Test?
Antigen assays identify particular proteins on the coronavirus’s surface. Because you can complete the test in under an hour to receive the test results, they are commonly referred to as rapid diagnostic tests. Antigen test results that are positive are quite specific; thus, you are almost certainly infected if you test positive.
While providing highly accurate answers in 15 to 30 minutes, antigen testing has a higher potential for false negative results than PCR tests. Once infected, a person “sheds” the viral load in their body; the amounts might change significantly throughout the infection. Testing too early (or late) can produce a false negative, although antigen tests can identify an infection that is actively spreading. Because they provide results in minutes, don’t require laboratory processing, and are less expensive upfront, antigen testing is still frequently regarded as the first line of defence. Even better, you can now order four antigen tests from the Department of Health and Human Services for free (tests expected to ship within 7-12 days).
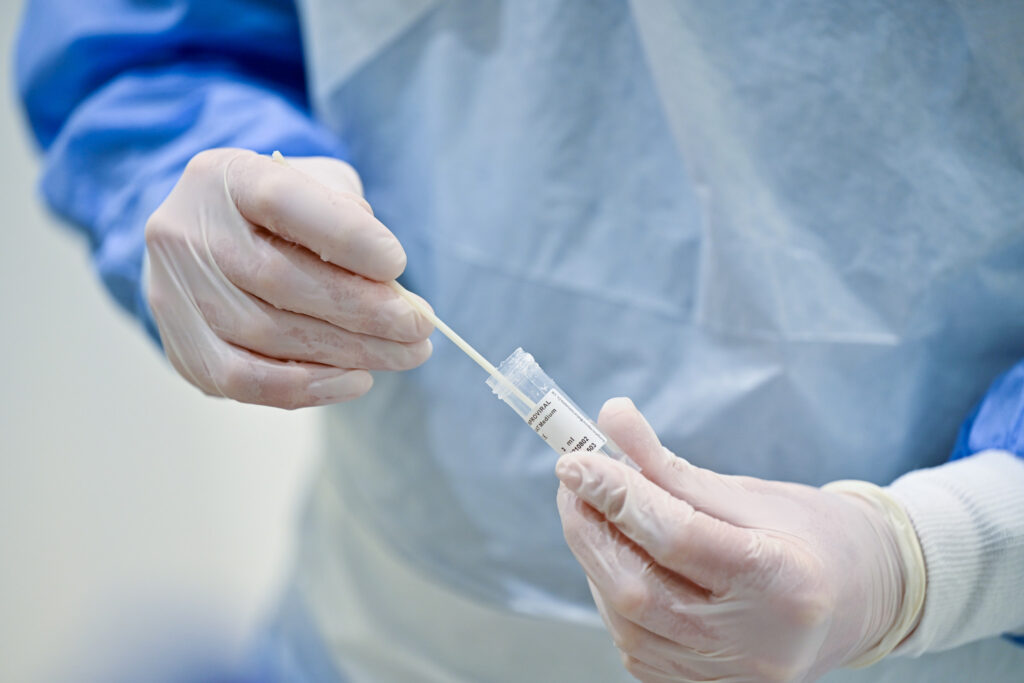
Major Disadvantages of Rapid Antigen Test
In contrast to the PCR test, the antigen test can only reveal whether you are infected with an active virus since the PCR test is more precise than the rapid antigen test in detecting asymptomatic cases or small virus levels.
Rapid antigen testing is less reliable and more likely to result in a false negative. Additionally, since the test only detects if the virus is active in your body, asymptomatic cases—those in which a person exhibits no symptoms—are more challenging to detect with the antigen test.
The Difference Between PCR And Antigen Tests
Technique, timing, and usage are typically where the distinctions lie. The cost can also change a lot. In contrast to the PCR test, which often takes a few days to produce findings, an antigen test is quick. While a PCR test looks for and increases the presence of the virus’s DNA, an antigen test scans the virus’s surface for particular proteins. For overseas travel, PCR testing is desirable or necessary.
You probably won’t get to pick the test you get if you go to a healthcare practitioner to get tested. There are a few causes for this. First, it can simply depend on whether the test is simpler to obtain or more common. Second, tests are chosen depending on the likelihood of detecting the infection.
PCR would be used in situations with a slim chance that a patient has the virus, but we want to be sure. We will pick an antigen to screen the patient as positive or negative if there is a high likelihood that they have the virus (i.e., if they are displaying symptoms). Getting tested is a crucial step in preventing the COVID-19 virus from spreading. PCR testing is recommended because they provide more accurate results; however, antigen tests also provide results quickly.